Installing Apache and PHP on Linux
-
- Last edited 4 years ago by MLR
-
-
- This page is a draft but has an approved version
| The web server delivers your BlueSpice installation to the user's browser. Without a web server, BlueSpice cannot be used. The source code of BlueSpice is based on the scripting language "PHP". This must also be installed on your server in order to operate BlueSpice. The steps listed here are required. |
Introduction
Apache or Nginx are available as web servers under Linux. BlueSpice can theoretically also be operated with Nginx, but in this documentation only Apache is treated in detail. Of course, you can also install Nginx with the appropriate expertise and operate it according to the here documented Virtualhost configuration of Apache.
| If "User is not in the sudoers file." type "su" in the terminal and execute. Write a "sudo" in front of a command. |
Installation
Install Apache and PHP using the Aptitude package manager with the following steps:
apt update; \
apt install apache2 \
libapache2-mod-php7.4 \
php7.4 \
php7.4-cli \
php7.4-common \
php7.4-curl \
php7.4-gd \
php7.4-intl \
php7.4-json \
php7.4-mbstring \
php7.4-mysql \
php7.4-opcache \
php7.4-tidy \
php7.4-xml \
php7.4-zip; \
apt clean
Configuring PHP
After installation, configure PHP. Open php.ini with a text editor of your choice (nano, vi), which, in our Debian version, is located in the directory /etc/php/7.3/apache2.
Find the following settings and change the values accordingly. If a setting is commented out with a semicolon in front of it, please remove it.
date.timezone = Europe/Berlin max_execution_time = 600 post_max_size = 128M upload_max_filesize = 128M
Set the value for 'date.timezone' according to your own time zone.
Save and exit the php.ini again. File:Setup:apache vhost bluespice free.txt
Configuring Apache
In this documentation, we assume the recommended installation with ShortURL. In this case, the root directory of the web server is in /var/www/bluespice, but the actual source code of BlueSpice is in /var/www/bluespice/w. This configuration is designed accordingly.
|
To configure a VirtualHost for BlueSpice, please proceed as follows:
- Change to the directory
/etc/apache2/sites-available. - In a text editor of your choice, open the file
bluespice.conf, which does not yet exist, and create it. Copy the entire contents of the following file into this new configuration file:- For BlueSpice free: apache_vhost_bluespice_free.txt
- For BlueSpice pro: apache_vhost_bluespice_pro.txt
- In rows 3 and 4, replace "SERVERNAME" and "SERVERALIAS" according to your server name and domain. If the server is explicitly operated with only one VirtualHost for BlueSpice, you can also completely remove these two lines.
- Save the file and close it.
If you do not have rights to save:
- Open a text editor of your choice.
- Copy the complete contents of the following file into this new configuration file.
- Bei BlueSpice free: apache_vhost_bluespice_free.txt
- Bei BlueSpice pro: apache_vhost_bluespice_pro.txt
- In rows 3 and 4, replace "SERVERNAME" and "SERVERALIAS" according to your server name and domain. If the server is explicitly operated with only one VirtualHost for BlueSpice, you can also completely remove these two lines.
- Save the file as
bluespice.confunder any file path and exit it. - In terminal, run the command
sudo mv /yourfilepath/bluespice.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available.
Delete the VirtualHost created by default during the Apache installation with the command a2dissite 000-default. Then activate the just created VirtualHost with the command a2ensite bluespice.
Next, activate the Module Rewrite, which we configured in the bluespice.conf, by entering the following command: a2enmod rewrite
Next, create the directory /var/www/bluespice(mkdir/var/www/bluespice) and restart Apache with the command service apache2 restart.
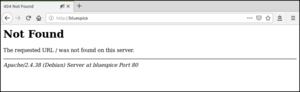
Next, call up the URL of your BlueSpice server. If configured correctly, Apache should respond to the request with the error message "Not found", which is completely correct at the time of installation.
Next step
If you have successfully completed all these steps, you can proceed to the next step " MariaDB".