You are viewing an old version of this page. Return to the latest version.
No categories assigned
Environment Variables (Windows)
-
- Last edited 6 years ago by MLR
-
< Setup:Installation Guide
Revision as of 14:44, 13 September 2019 by Mlink-rodrigue (talk | contribs) (Mlink-rodrigue moved page Setup:Installation Manual/Services and system configuration/Environment Variables to Setup:Installation Guide/Services and system configuration/Environment Variables without leaving a redirect)
For using console commands for PHP ans MySQL in a comfortable way, some settings in the environment variables should be done. This document describes how to do this.
Tips for this Document
- Please, read this manual completely and work through the single installation steps one after another.
Figure out Paths
Please try to figure out in which paths of your Windows installation the following files are located:
- php.exe
- mysql.exe
This document uses this paths as an example for the description:
- C:\Program Files (x86)\PHP\php-5.6.30\php.exe
- C:\Program Files\MariaDB 10.1\bin\mysql.exe
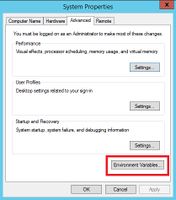
Enter Environmental Variables
- Press the key combination "Windows + R" to start the input request
- Start the program "SystemPropertiesAdvanced.exe"
- Click at "Environment Variables"
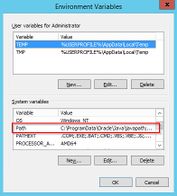
- Open the variable "Path" at "System variables" with a double click
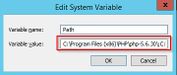
- With Windows 2012: In the line "Value of Variables", add the paths to php.exe and mysql.exe, separated by semicolon, directly at the beginning of the line. Regarding the path example, this would be "C:\Program Files (x86)\PHP\php-5.6.30\;C:\Program Files\MariaDB 10.1\bin\;"
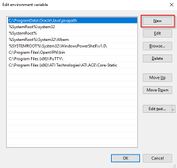
- Windows 2016 and above: Add two new entries with their respective pathnames
- Close all windows by clicking on "OK"
- Restart the command line
Now you should be able to call up the commands "php" and "mysql" without problems in the command line.